Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, CAEP, Shanghai 201899, People’s Republic of China
The use of broadband laser technology is a novel approach for inhibiting processes related to laser plasma interactions (LPIs). In this study, several preliminary experiments into broadband-laser-driven LPIs are carried out using a newly established hundreds-of-joules broadband second-harmonic-generation laser facility. Through direct comparison with LPI results for a traditional narrowband laser, the actual LPI-suppression effect of the broadband laser is shown. The broadband laser had a clear suppressive effect on both back-stimulated Raman scattering and back-stimulated Brillouin scattering at laser intensities below 1 × 1015 W cm-2. An abnormal hot-electron phenomenon is also investigated, using targets of different thicknesses.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2024, 9(1): 015602

1 北京应用物理与计算数学研究所,北京 100094
2 北京大学 应用物理与技术研究中心 高能量密度物理数值模拟教育部重点实验室工学院,北京 100871
3 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心,四川 绵阳 621900
4 中国工程物理研究院 上海激光等离子体研究所,上海 201800
5 中国矿业大学(北京),北京 100083
6 中国海洋大学 数学科学学院,山东 青岛 266100
7 安徽大学 物理与材料科学学院,合肥 230039
激光聚变有望一劳永逸地解决人类的能源问题,因而受到国际社会的普遍重视,一直是国际研究的前沿热点。目前实现激光惯性约束聚变所面临的最大科学障碍(属于内禀困难)是对内爆过程中高能量密度流体力学不稳定性引起的非线性流动的有效控制,对其研究涵盖高能量密度物理、等离子体物理、流体力学、计算科学、强冲击物理和高压原子物理等多个学科,同时还要具备大规模多物理多尺度多介质流动的数值模拟能力和高功率大型激光装置等研究条件。作为新兴研究课题,高能量密度非线性流动问题充满了各种新奇的现象亟待探索。此外,流体力学不稳定性及其引起的湍流混合,还是天体物理现象(如星系碰撞与合并、恒星演化、原始恒星的形成以及超新星爆炸)中的重要过程,涉及天体物理的一些核心研究内容。本文首先综述了高能量密度非线性流动研究的现状和进展,梳理了其中的挑战和机遇。然后介绍了传统中心点火激光聚变内爆过程发生的主要流体力学不稳定性,在大量分解和综合物理研究基础上,凝练出了目前制约美国国家点火装置(NIF)内爆性能的主要流体不稳定性问题。接下来,总结了国外激光聚变流体不稳定性实验物理的研究概况。最后,展示了内爆物理团队近些年在激光聚变内爆流体不稳定性基础性问题方面的主要研究进展。该团队一直从事激光聚变内爆非线性流动研究与控制,以及聚变靶物理研究与设计,注重理论探索和实验研究相结合,近年来在内爆重要流体力学不稳定性问题的解析理论、数值模拟和激光装置实验设计与数据分析等方面取得了一系列重要成果,有力地推动了该研究方向在国内的发展。
激光聚变 惯性约束聚变 流体力学不稳定性 高能量密度物理 非线性流动 辐射流体力学 内爆物理 laser fusion inertial confinement fusion hydrodynamic instability high-energy-density physics nonlinear flow radiation hydrodynamics implosion physics 强激光与粒子束
2021, 33(1): 012001
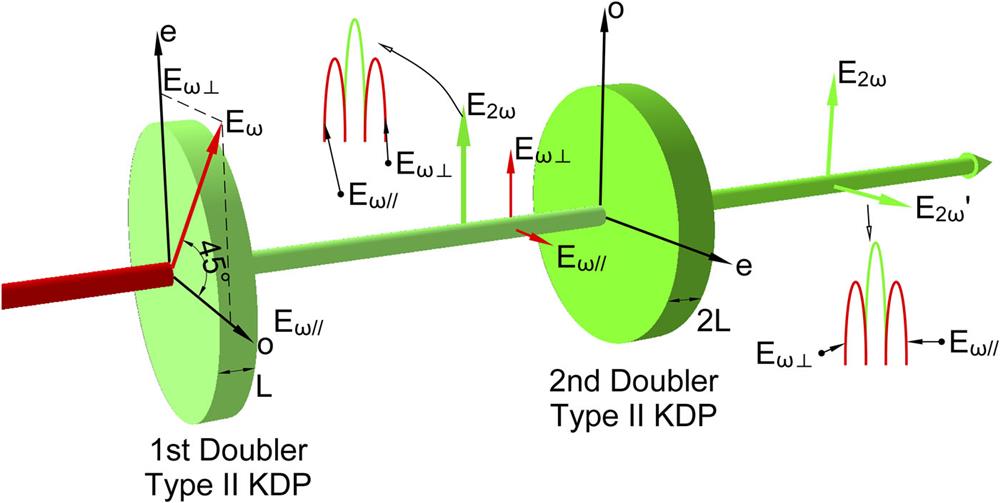
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201899, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Crystal Materials, Shandong University, Jinan 250100, China
3 School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China
The use of low-coherence light is expected to be one of the effective ways to suppress or even eliminate the laser–plasma instabilities that arise in attempts to achieve inertial confinement fusion. In this paper, a review of low-coherence high-power laser drivers and related key techniques is first presented. Work at typical low-coherence laser facilities, including Gekko XII, PHEBUS, Pharos III, and Kanal-2 is described. The many key techniques that are used in the research and development of low-coherence laser drivers are described and analyzed, including low-coherence source generation, amplification, harmonic conversion, and beam smoothing of low-coherence light. Then, recent progress achieved by our group in research on a broadband low-coherence laser driver is presented. During the development of our low-coherence high-power laser facility, we have proposed and implemented many key techniques for working with low-coherence light, including source generation, efficient amplification and propagation, harmonic conversion, beam smoothing, and precise beam control. Based on a series of technological breakthroughs, a kilojoule low-coherence laser driver named Kunwu with a coherence time of only 300 fs has been built, and the first round of physical experiments has been completed. This high-power laser facility provides not only a demonstration and verification platform for key techniques and system integration of a low-coherence laser driver, but also a new type of experimental platform for research into, for example, high-energy-density physics and, in particular, laser–plasma interactions.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2020, 5(6): 065201
强激光与粒子束
2020, 32(1): 011004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, CAEP, Shanghai 201800, China
2 IFSA Collaborative Innovation Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing 100094, China
Although the streaked optical pyrometer (SOP) system has been widely adopted in shock temperature measurements, its reliability has always been of concern. Here, two calibrated Planckian radiators with different color temperatures were used to calibrate and verify the SOP system by comparing the two calibration standards using both multi-channel and single-channel methods. A high-color-temperature standard lamp and a multi-channel filter were specifically designed for the measurement system. To verify the reliability of the SOP system, the relative deviation between the measured data and the standard value of less than 5% was calibrated out, which demonstrates the reliability of the SOP system. Furthermore, a method to analyze the uncertainty and sensitivity of the SOP system is proposed. A series of laser-induced shock experiments were conducted at the ‘Shenguang-II’ laser facility to verify the reliability of the SOP system for temperature measurements at tens of thousands of kelvin. The measured temperature of the quartz in our experiments agreed fairly well with previous works, which serves as evidence for the reliability of the SOP system.
laser-induced shock waves shock temperature measurement streaked optical pyrometer High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2019, 7(3): 03000e49
中国工程物理研究院上海激光等离子体研究所, 上海 201800
基于神光Ⅱ升级装置,研究了纳秒/皮秒双束激光联合驱动双层靶的伽马(γ)辐射特征。利用ns束激光与CH薄膜靶相互作用,产生大尺度近临界密度等离子体,然后将ps束激光作用在该等离子体上,产生高能电子,高能电子穿过2 mm厚的Au靶,通过轫致辐射产生γ射线。对不同方向的γ辐射能谱和靶室外的γ辐射剂量分布进行实验测量,发现γ辐射集中在激光前冲方向,具有较小的发散角,而且在该方向上高能段的γ辐射较强。这说明双层靶的设计可以提高ps束激光与等离子体的能量耦合效率,提高高能电子温度,增加高能电子数目,有利于高能段γ辐射在ps束激光的前冲方向集中。另外,在靶室外距离靶点1.25 m处测到的50 keV以上γ辐射的单发次最大剂量为277 μGy。本研究结果对γ辐射的防护和应用具有参考价值。
激光器 双层靶 γ辐射; 能谱 剂量 角分布
中国工程物理研究院 上海激光等离子体研究所, 上海 201800
液氘在高压下有丰富的电学光学性质。利用反射率和相对介电函数关系并从广义极化角度出发初步建立了计算低Z材料电导率的简易模型; 在神光-Ⅱ装置上利用第九路激光冲击加载液氘材料并测量了其在强激光冲击下的高压状态参数和反射率。结合上述理论模型和实验, 研究了高压下液氘的电离度和电导率。结果表明, 液氘在约70 GPa时的电导率约为2.87×105 (Ω·m)-1, 已呈现出较为明显的金属电导特性。显然, 冲击加载下液氘从绝缘分子态开始电离并向金属氘转变发生在更低的压强。
电导率 高压 相对介电函数 反射率 强激光加载 conductivity high pressure relative dielectric function reflectivity high power laser-driven shock loading 强激光与粒子束
2017, 29(8): 082002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, Shanghai 201800, P.R. China
High precision polystyrene equation of state data were measured using laser-driven shock waves with pressures from 180 GPa to 700 GPa. α quartz was used as standard material, the shock wave trajectory in quartz and polystyrene was measured using the Velocity Interferometer for Any Reflector (VISAR). Instantaneous shock velocity in quartz and polystyrene was obtained when the shock wave pass the interface. This provided ~1% precision in shock velocity measurements.
Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): 259
Author Affiliations
Abstract
中国工程物理研究院 上海激光等离子体研究所, 上海 201800
The fabrication of metal film steps used in equation of state experiment targets was investigated. The metal film step of hundreds of microns width was cut by picosecond laser processing technology. The factors of generating heat effect in the processing were analyzed. The processing parameters were as follows: power 0.5 W, pulse width 10 ps, wavelength 355 nm, and scanning speed 100 mm/s. Two metal films of 400 and 120 microns width were obtained in the experiment. The measurement results show that the width of metal film can be precisely controlled and the quality of metal film surface before and after cutting was the same.
状态方程 靶 薄膜 皮秒激光 equation of state target film picosecond laser Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2014, 12(1): 022009
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, P.O. BOX 800-229, Shanghai 201800, China
In this paper, we systematically study preheating in laser-direct-drive shocks by using a velocity interferometer system for any reflector (VISAR). Using the VISAR, we measured free surface velocity histories of Al samples over time, 10–70 lm thick, driven directly by a laser at different frequencies (2x, 3x). Analyzing our experimental results, we concluded that the dominant preheating source was X-ray radiation. We also discussed how preheating affected the material initial density and the measurement of Hugoniot data for high-Z materials (such as Au) using impedance matching. To reduce preheating, we proposed and tested three kinds of targets.
Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2014, 12(1): 082708





